Table of Contents
- What Are Remote Monitoring Solutions?
- Key Components of Modern Monitoring Systems
- How Remote Monitoring Improves Safety and Security
- Benefits for Facility Managers
- Overcoming Common Challenges
- Industry Examples and Use Cases
- Future Trends in Remote Monitoring
- Getting Started with Monitoring Technologies
What Are Remote Monitoring Solutions?
Today’s facility managers oversee complex environments where uptime, safety, and efficiency are vital. IBM: What is Remote Monitoring? illustrates a new generation of tools that enable 24/7 supervision of assets from any location. These solutions use smart sensors, real-time communication, and advanced data analytics to provide actionable insights, helping decision makers protect resources and ensure high performance. They offer visibility across various sites, from machinery to security, and reduce the need for on-site oversight by automatically collecting and analyzing data, which improves issue detection and speeds responses. Forbes reports that the use of these technologies is expanding rapidly due to their cost-saving and operational benefits. To learn more about remote monitoring, visit http://www.quickresponse.net/monitoring-solutions/.
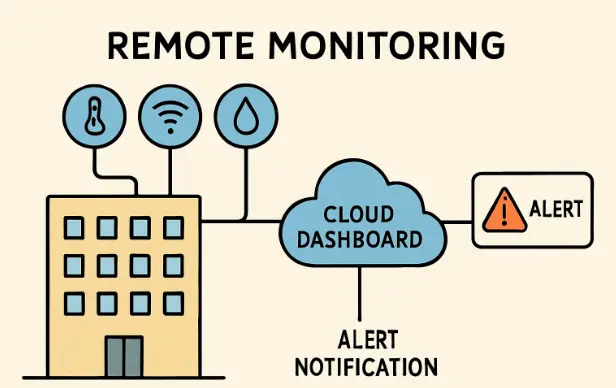
Key Components of Modern Monitoring Systems
- Sensors: Modern sensors track temperature, humidity, energy usage, movement, and specialized variables such as air quality or vibration in mechanical systems.
- Connectivity: Secure data transmission via Wi-Fi, cellular, or Ethernet is vital. This connectivity ensures that facility conditions are monitored continuously and alerts can be issued instantly.
- Cloud Platforms: Centralized dashboards and cloud storage allow for streamlined data analysis, trend identification, and accessible reporting for teams across multiple locations.
- Integration Capabilities: Advanced APIs and compatible software modules enable remote monitoring platforms to synchronize with maintenance, energy management, and asset tracking systems.
Redundancy is frequently built into these systems to minimize single points of failure, and the best platforms offer customizable notifications, allowing facility managers to receive only the most relevant alerts.
How Remote Monitoring Improves Safety and Security
A key advantage of remote monitoring is its transformative impact on facility safety and security. With 24/7 surveillance, facility threats—whether related to unauthorized access, equipment malfunction, or environmental hazards—are detected and communicated instantly. Research from Security Magazine highlights that organizations using remote monitoring experience faster incident resolution, better regulatory compliance, and reduced risk of operational disruptions. Automated alerts ensure that facility managers have immediate information about potential emergencies, enabling swift and coordinated responses.
Benefits for Facility Managers
- Real-Time Alerts: Receive instant notifications about equipment faults or suspicious activities, allowing problems to be quickly addressed before they escalate.
- Cost Savings: Less need for routine in-person inspections translates to lower labor expenses. Automated detection of inefficiencies or minor faults helps avoid expensive emergency repairs.
- Predictive Maintenance: Harnessing analytics to identify usage patterns and wear factors enables teams to schedule repairs and maintenance before breakdowns occur, prolonging equipment lifespan.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Detailed logs and trend reports empower managers to allocate resources more efficiently and plan upgrades that yield long-term savings.
For facility management professionals, these benefits drive improved operational continuity and reliability, reducing the risk of costly downtime and enhancing the overall tenant or employee experience.
Overcoming Common Challenges
As facilities transition to smarter systems, cybersecurity emerges as a key concern. Every connected device can be an entry point for cyber threats. Routine firmware updates, two-factor authentication, and robust password policies are critical for safeguarding sensitive data. Another challenge is integrating with legacy infrastructure—older systems may not support modern APIs or cloud protocols, complicating harmonization. However, partnering with experienced IT professionals and choosing solutions designed for integration can help bridge technological gaps and ensure a stable rollout.
The significance of well-executed integration is underscored by guidance from IoT For All, which stresses the importance of open standards and proper training when deploying new monitoring technologies at scale.
Industry Examples and Use Cases
Remote monitoring’s versatility means it is found everywhere—from large hospitals to remote agricultural sites. Healthcare facilities use it to ensure life-saving equipment is functional and the environments of critical care areas remain controlled. Retail environments deploy these systems to continuously monitor security after hours, reducing losses due to theft or vandalism. In smart agriculture, sensors automate irrigation by monitoring soil moisture and weather, maximizing yields while reducing water waste. Such diverse use cases highlight the adaptability and ROI of remote monitoring across sectors.
Future Trends in Remote Monitoring
Technology in this space is advancing quickly. The proliferation of IoT devices means facilities have access to richer, more granular data in real time. AI-powered platforms are being developed to enhance predictive capabilities, allowing issues to be anticipated and addressed before major failures occur. There is also a shift toward mobile-first solutions and the use of wearable devices, making monitoring accessible at any time, from anywhere. As more industries recognize the value of interconnected monitoring, expect continued growth in interoperability between systems, deeper automation, and even more intuitive user interfaces for facility teams.
Getting Started with Monitoring Technologies
Organizations should first identify their critical assets and security pain points. Mapping areas needing real-time oversight helps prioritize investments. When choosing a platform, consider its compatibility, scalability, and ease of integration. Piloting solutions in low-risk settings helps build confidence and identify operational issues. Ongoing education and collaboration between facilities and IT ensure smooth adoption. Remote monitoring is now a crucial component of modern facility management. Using advanced tech and best practices, facilities can improve safety, efficiency, and ROI, enhancing operational resilience now and later.
Also Read-From Code to Customer: Building Awareness in Technical Markets